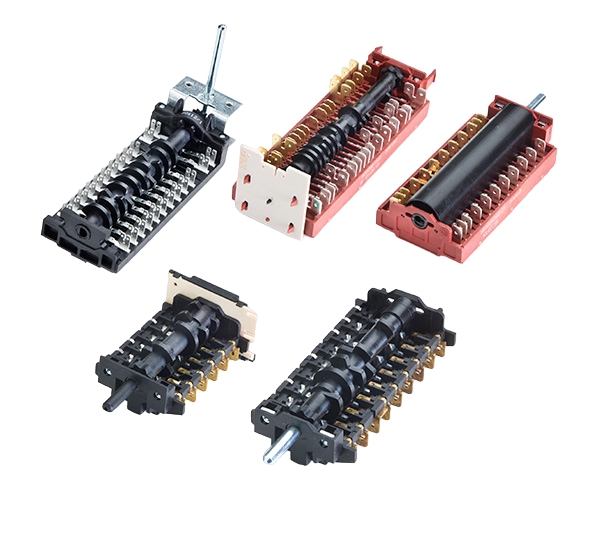
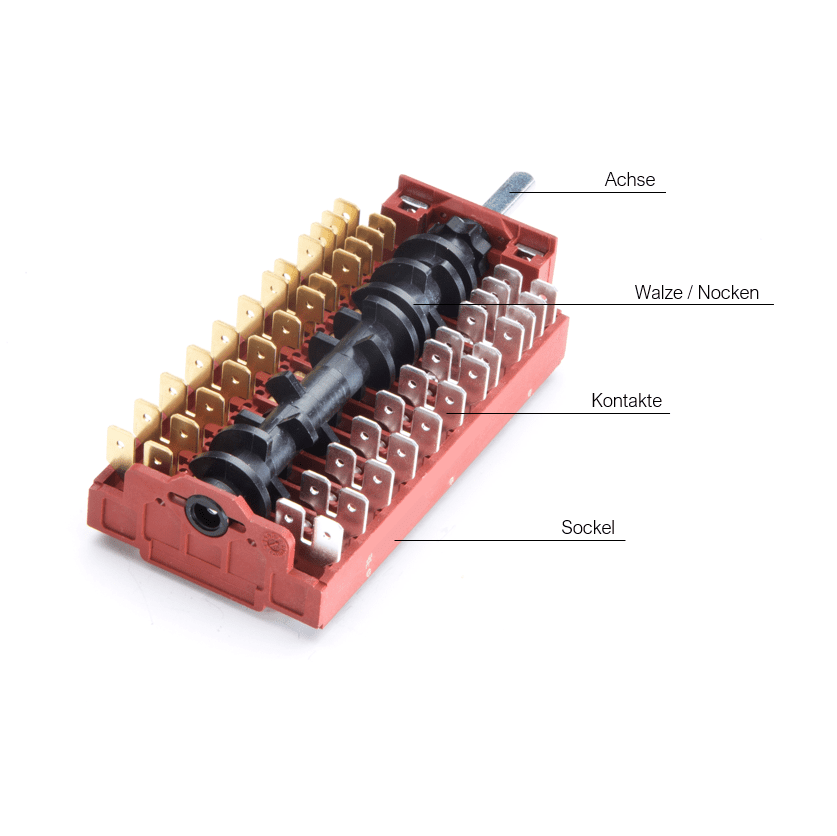
How do rotary switches work?
By turning the axis of the rotary switch, the so-called ‘cams’ are moved, which are responsible for the switching of the contacts. Each cam has a unique shape that fits onto the respective switching contact. When a cam reaches the switch contact, it pushes it to a certain position, changing the circuit of the switch.
Depending on the number of cams and contacts, the rotary switch can have different switching positions, which affect the circuit of the switch in different ways.
The function of a rotary switch depends on its design and use. Some rotary switches can be used, for example, to control electrical signals, such as volume, brightness, speed or temperature. Other rotary switches can be used to control electrical devices or machines, by activating or deactivating the circuit.